Engine emissions are a critical concern in the heavy-duty trucking sector, particularly with upcoming regulations such as EPA GHG ’27, which mandates an 80% reduction in NOx emissions. Despite potential political changes that could alter compliance timelines, fleets need to start adapting now for these inevitable shifts. Effective maintenance of aftertreatment systems—especially the diesel particulate filter—can aid fleet managers in maximizing vehicle availability and complying with new regulations.
Proactive vs. Reactive Truck Aftertreatment Maintenance
JT Roberson, strategic sales manager at Ceramex, outlines two distinct approaches to DPF and aftertreatment maintenance among fleet operators:
- Reactive aftertreatment maintenance: Fleets adopting this method only attend to DPF failures as they occur, resulting in immediate replacements. This strategy may lead to significant upfront expenses if regulatory changes require rapid compliance.
- Proactive aftertreatment maintenance: These fleets engage in planned preventative maintenance, allowing them to spread out costs and prolong the lifespan of their equipment. They enjoy benefits such as longer intervals between service requirements, decreased downtime, and an advantage in a marketplace where emission standards are becoming stricter.
“Once the EPA 2027 regulations are enacted, reactive fleets will face sudden and significant costs to ensure compliance,” Roberson remarked. “In contrast, those with preventative maintenance strategies will have a competitive edge, facing regulatory impacts more gradually while their filters maintain efficiency for longer periods.”
While aftertreatment servicing poses challenges for many fleets, their responses to issues can worsen the situation. Simply advising to “Run a regen!” should not be a blanket solution for aftertreatment failure codes. Roberson also pointed out that there are alternatives to the expensive process of replacing a DPF.
Diesel Particulate Filter Restoration: How It Works
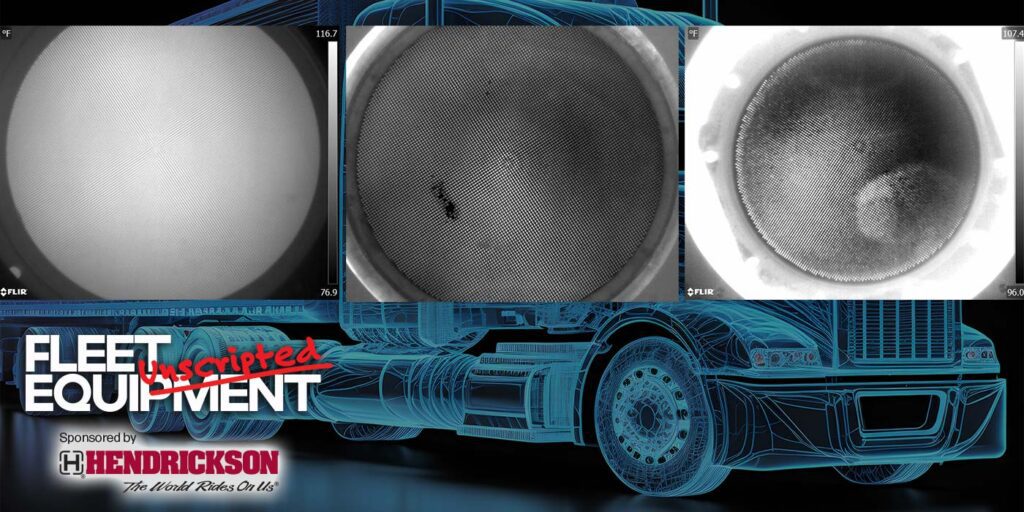
The process of cleaning a diesel particulate filter typically starts with a meticulous cleaning that removes soot and ash without introducing further contaminants. According to Roberson, the Ceramex cleaning method utilizes deionized water to safeguard sensitive filter materials. Following cleaning, the filter undergoes drying and flow testing to confirm it meets operational specifications. Ceramex also employs a unique advanced inspection method, similar to an internal “x-ray,” to identify any cracks or structural issues, providing clients opportunities for further action if problems are detected. Finally, technicians remove old gaskets and buildup to prepare the filter for reinstallation.
Leveraging Aftertreatment Data for Making Maintenance Decisions
An in-depth review of a diesel particulate filter’s cleaning during restoration can reveal valuable insights regarding truck service. Roberson highlighted that he can provide detailed images showing the filter’s condition before and after cleaning, enabling fleets to assess the levels of ash and soot or detect any structural damage.
Fleets that consistently evaluate these insights can spot trends of premature loading or ongoing filter damage, which may indicate underlying engine or operational problems, prompting necessary adjustments in engine maintenance or operational practices.
For more information on aftertreatment system services, check out the accompanying video.